Use these 67 types of keywords strategically for your SEO optimization. If you do, you’re rankings will climb through the roof.
The fact is, today’s businesses rely heavily on internet traffic to get customers.
And the key to getting that traffic is by knowing how to rank high on the mother of all search engines… Google.
In the past, when Google’s’ algorithm wasn’t so sophisticated, simply optimizing your website for the right keywords would get it to rank high quickly.
SEO (search engine optimization) was almost as simple as writing and ranking.
That doesn’t work anymore.
Well, unless, you actually know the right types of keywords.
Then your site can still rank high based on the keywords and content of your site.
There are some other factors but at the end of the day, you have to tell Google what your page is about without ruining the user experience.
The great thing about these different types of keywords is that unlike other SEO information, this will be relevant regardless of what year you are reading it because types of words don’t change much like other algorithm tweaks.
The right types of keywords, when sprinkled through your posts and site, can help you rank before you even start to get backlinks.
Backlinks are important, but maybe not as important as you think.
If you’re obsessed with backlinks, check out this video:
Hopefully, that video changed your perspective a little concerning content and link building.
The most valuable asset you have is great content that a significant number of people are searching for AND limited competition from other sites.
That’s basically how any competitive, sustainable business is set up:
You provide a product people need and want with minimal competitors.
So, how do you identify those content opportunities before you write the content?
You do some research on words that a significant number of people are searching for, but few or no other site has.
That’s a good indicator of content gaps you can take advantage of.
That being said, this ultimate guide on the various types of keywords isn’t about tricking Google.
Instead, it’s about understanding the types of keywords you can base your content on, depending on what you intend to achieve (lower bounce rate, high traffic, high conversion, etc…).
Important note: Since this is an extensive list of keyword types, you shouldn’t try to optimize your content for all of them. Instead, focus on the main types of keywords that will serve your audience the best.
You May Also Enjoy These Ultimate Guides:
– The Ultimate Guide to Global Marketing
– The Ultimate Guide to Scaling Your Business with Direct Marketing
Use These 67 Types of Keywords in
SEO Optimization For Explosive Growth
1. User Intent Keywords
These are among the most basic types of keywords in SEO optimization.
Understanding the underlying reason why someone is searching for a particular word or phrase is vital in crafting content specifically suited to that user.
As you may know, Google updates it’s algorithm to focus on quality and user intent.
When evaluating these types of keywords, consider the following:
i. Specific User Intent
Some words have specific user intent, meaning people searching are looking for search results focused on a specific issue.
Often, this applies to long tail keywords (which typically have lower search volumes).
Usually, you can understand specific user intent by looking at the top Google SERPs (search engine result pages).
The top search results will generally feature the type of content that matches user intent.
For instance, look at these search results for the phrase “how to start a small business without money”:


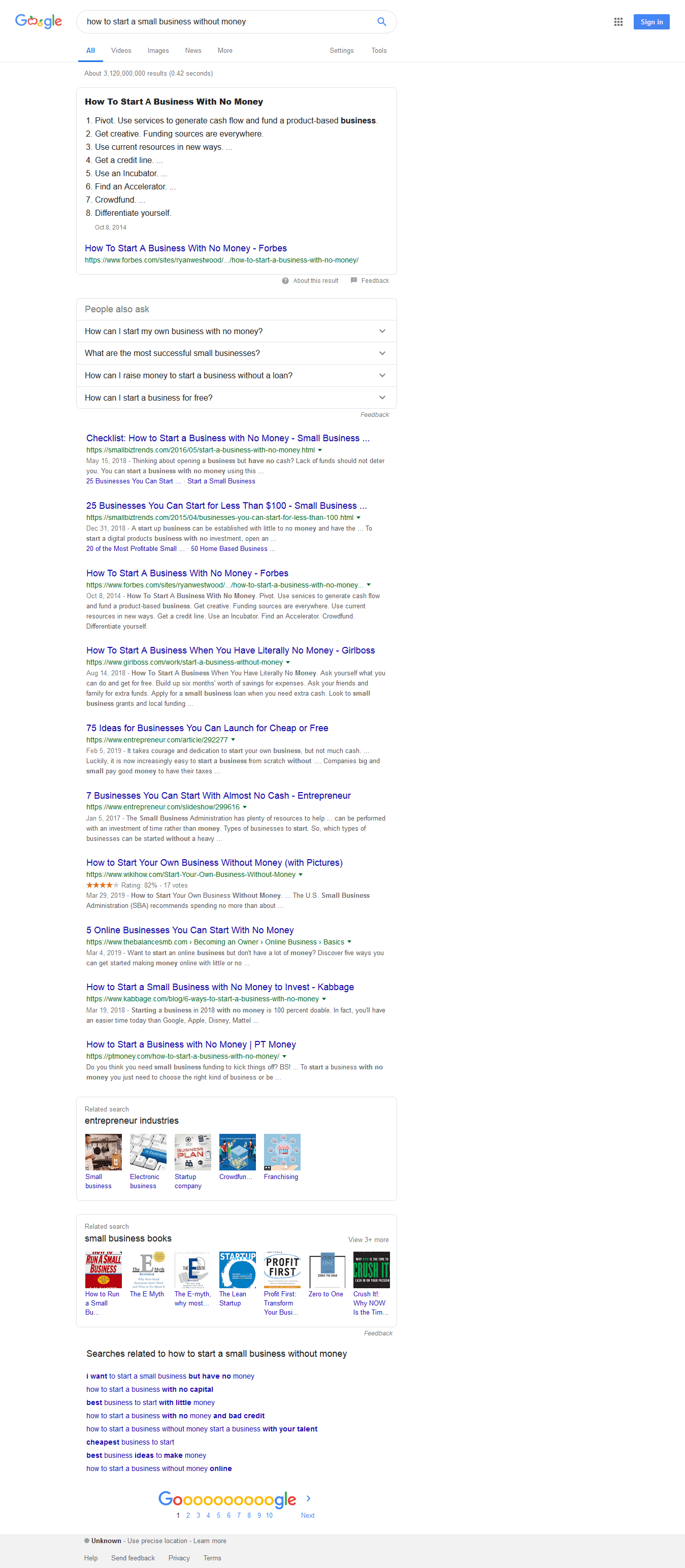

Ranking high for such a phrase is possible if you provide in-depth content on the issue, particularly when very few sites cover the searcher intent effectively.
ii. Mixed User Intent
You’ll likely be able to find mixed user intent searches with high-traffic words or search phrase.
That’s one reason it can be incredibly difficult to optimize your content for such keywords.
People searching are looking for solutions to multiple issues.
However, it’s also a huge opportunity.
You can write up an article and title that aggregates the multiple issues people want.
Simply look through the search results and find out what different issues are covered in the top-ranking articles.
Then write a comprehensive article that covers multiple issues.
An example of this might be how to lose weight AND not be hungry.
Those are two different (but connected) things.
The user intent of that Google search wants to lose weight but they also want to not be hungry while doing it.
2. Buyer Journey/ Sales Funnel Keywords
These are probably the most important types of keywords in SEO because they set the basic foundation of a blog or website.
Such keywords help you provide a complete collection of content that serves the needs of your target customers through the entire buyer journey:
- awareness
- consideration
- decision/ purchase
- post-purchase
Each stage leads on to the next one, as illustrated here:
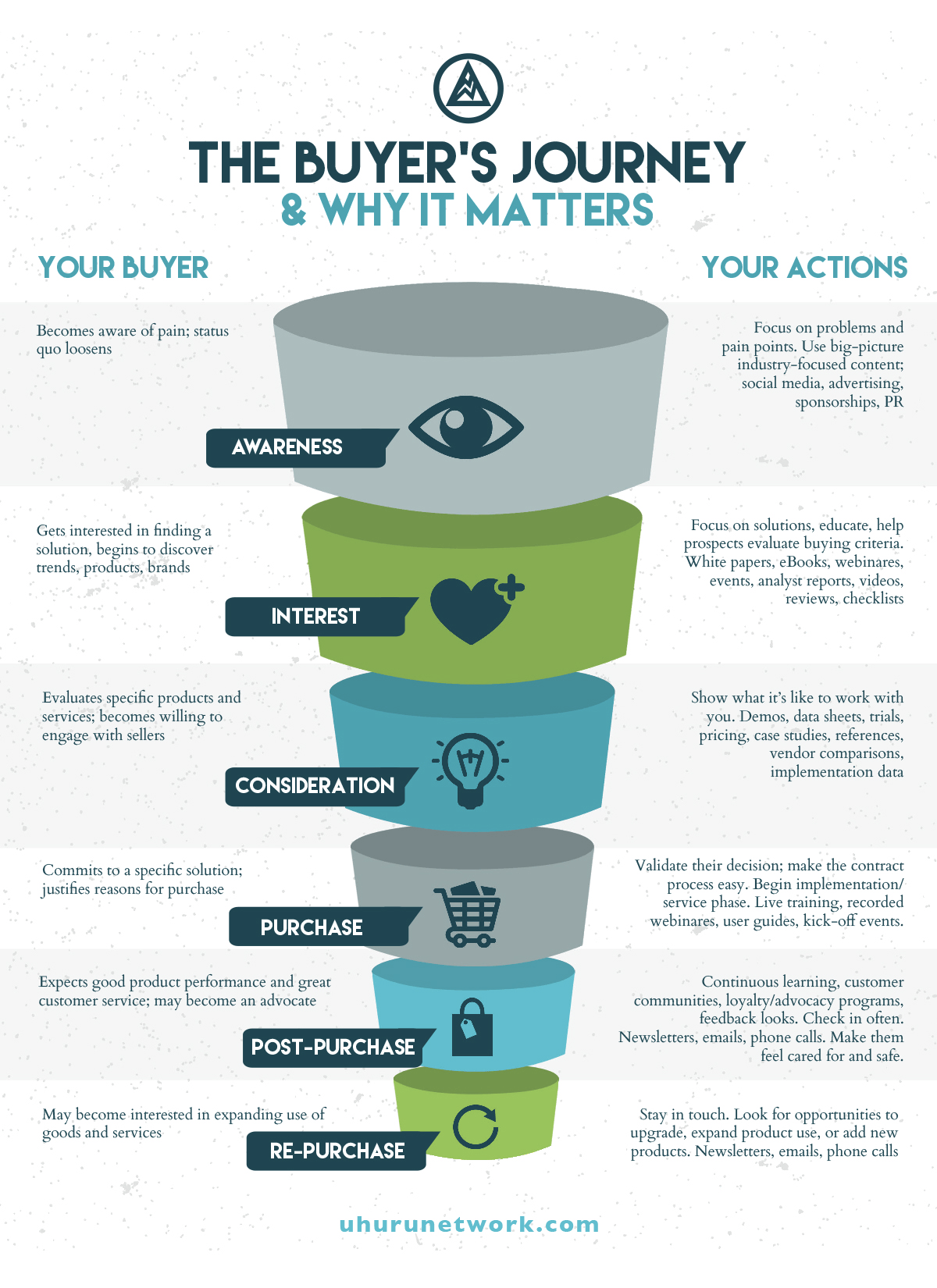

Here’s an overview of how you optimize for the buyers journey.
i. Informational Posts
These posts focus on people searching for information about the topic.
The types of keywords you use for these posts will match up with the awareness stage of the buyer journey.
They typically provide general information around your niche.
Many times, these target words and phrases are easy to identify for SEO.
These types of keywords often have the words “how to,” “why is,” “who are”, “who is,” “where to,” and so on.
Providing content around your topic that starts with these phrases will help your website get a steady stream of new potential clients who may be at the beginning stages of the buyers journey.
If you look at our site structure, we focus a lot on “how to” topics around our niche.
ii. Navigational Keywords
Navigational keywords typically indicate that the person searching has moved on from the awareness stage and is now in the consideration phase.
The person is considering different options and may be closer to a buying decision.
Without targeted content, you could be losing many potential customers because they’re closer to the goal line than those just becoming aware of your topic or niche.
We also use this strategy quite a bit.
Here’s a list of a few navigational words:
- best
- cheapest
- pros and cons
- X vs. Y
- [brand name]
- review
- price
- testimonials
iii. Transactional Types of Keywords
Transactional searches indicate a person who is ready to buy (woo-woo)!
You definitely need to optimize for these types of words on your sales page.
Typical keywords in this category include words such as:
- buy
- coupons
- sale
- discount
- download
- where to buy
- [service/ product] [location]
iv. Post-Purchase Words
These types of keywords are often disregarded, yet studies show that retaining customers is five times cheaper than getting new customers.
Post-purchase words serve people who are already using your products or services.
In fact, when you provide content around these types of keywords, you may also win over your competitors’ existing customers.
You’ll be providing information that any loyal client would want to have.
The content strategy is typically to write informational posts, with a focus on maintaining your product or service.
The words you’ll likely find in this keywords category include:
- troubleshooting
- loyalty program
- how to fix or repair
3. LSI Keywords & SEO Optimization
Once you provide content around the core needs of your target audience, you need to think one step ahead.
That’s where LSI (latent semantic indexing) keywords come in.
Latent semantic indexing is basically a way for a search engine to look at your semantics, (the actual language and verbiage of the post) in order to figure out the main idea- what is the post really about (not based on keyword density but based on meaning).
Was that clear as mud?
Hopefully it made sense.
LSI keywords guide you in providing content that answers all the extra questions your audience has.
This way, the audience doesn’t have to click on to competitor sites to get more information.
The following classifications explain how to uncover these types of keywords in SEO optimization.
i. Upstream Keywords
Where did readers come from before they clicked on to your content?
Why not include a brief review of the information from the page they previously came from into your content?
These types of keywords are called upstream keywords and can be very powerful.
One way of identifying such upstream content is finding out which pages link to your content or to content similar to yours.
ii. Downstream Keywords
After reading your content, where do readers go?
Here too, you can include the information from the pages people go to, into your content.
Hopefully, that will keep the reader from needing to go to a different site.
It will increase your time on site and dwell time.
To identify such downstream content, check which pages you link out to.
One way to easily do this is to check your exit links and how often they are clicked per month.
If that’s too difficult, just type your keywords into google and look at related searches:

You can also check out the “People also ask” section:

iii. Vertical Keywords
These types of keywords are what people often think of when LSI keywords are mentioned.
The keywords here feature ideas within your specific niche.
This is one way search engines figure out which niche to classify your page in.
Without this, it would be hard to tell whether the mention of a term like “apple” in your article refers to the company or the fruit or somebody being a bad apple (which is technically neither).
iv. Horizontal Keywords
Many times, an issue in one niche has relevance to other niches.
For example, finance is an essential element in business as well as relationships.
If you’re covering a topic with extensive relevance to multiple niches, you’ll certainly use horizontal types of keywords.
By using SEO optimization strategies with these words, you’ll expand your target audience and potential traffic.
When you expand your audience this way, I call it it collateral traffic.
4. User-Defined Keywords
User-defining keywords are valuable in targeting the right audience.
The term means you are looking at the data of who your users are, then crafting content specifically for them.
First, you need to figure out who your audience is.
You can use social media insights (including Facebook/Twitter audience insights) and Google Analytics data from your site:
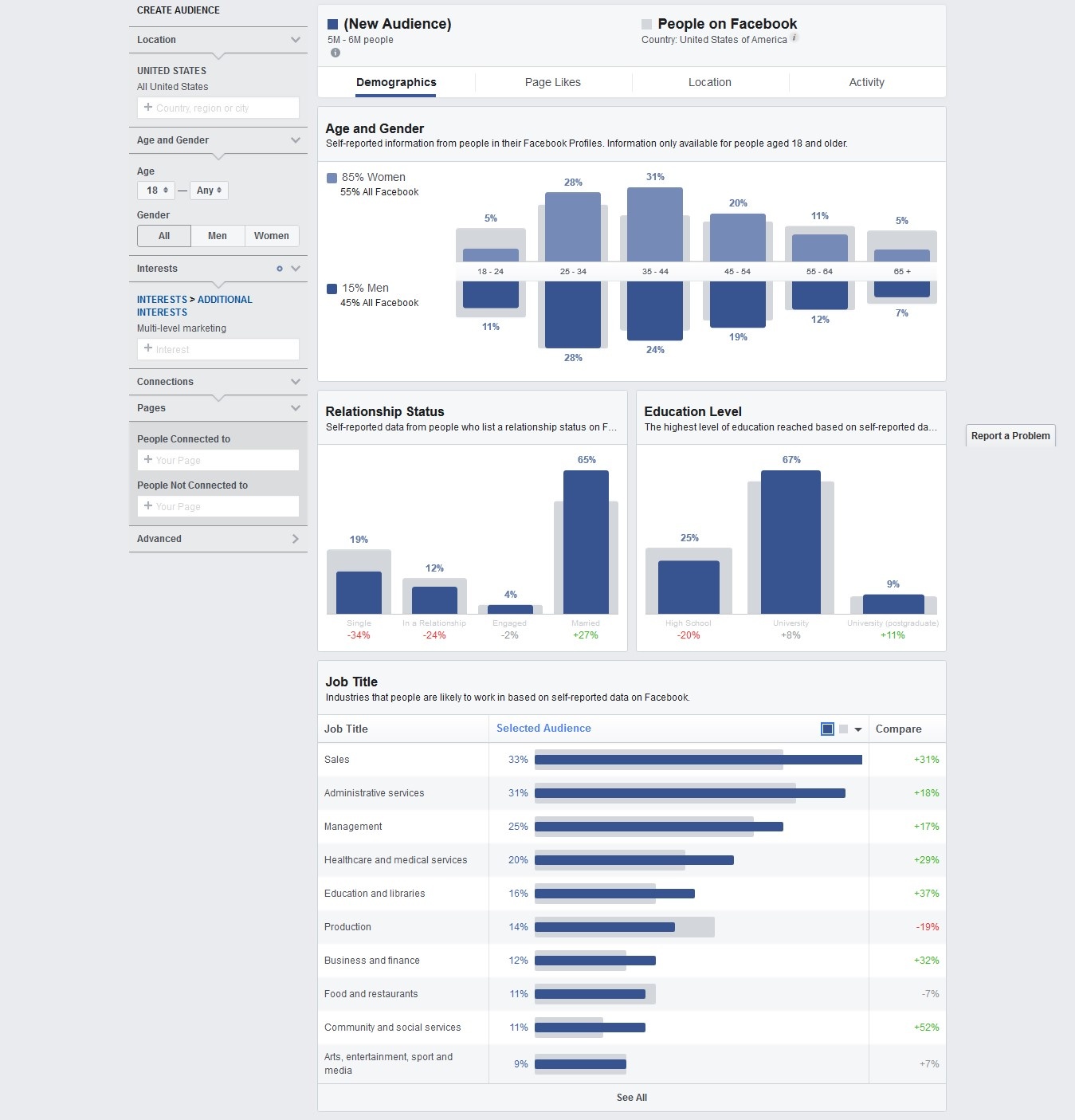

Once you have a good handle on what your typical user is, you just craft content specifically suited to them.
Knowing your audience will help you target keywords that your audience is likely to search for.
These types of keywords in SEO optimization can be very valuable, especially if you’re able to eventually achieve topical authority on any of them.
i. Occupational Words
This is pretty much self-explanatory.
People in a specific occupation are sure to search for specific details related to their occupation.
For instance, teachers are sure to search for issues regarding education.
If you’re writing on a topic that’s not directly related to your target audiences’ occupation, you should look for types of keywords that merge the two: your topic and the target audience’ occupation.
This way, you’ll get the right people to read your content.
For example, you could write an article entitled “how to save money”. This would target the entire population and competition for this phrase would be fierce.
Or you could write “how to save money: Teacher edition” and it narrows your audience and your potential competition.
ii. Social Status
The same case applies with social status.
Someone who values a life of luxury will likely not search for budget or cheap products.
Hence, you want to base your content around luxury products, in order to get the eyeballs of those audiences.
iii. Financial Status/ Income
This is similar to social status.
People earning a high incomes will live in higher value neighborhoods, buy more expensive vehicles, and eat out in pricier restaurants, among other things.
By understanding these details, you’ll know which type of searches they’ll be typing into Google.
Focus on those search terms to produce content that specifically resonates with them.
iv. Age
If your website is designed for a specific age group, you must understand their entire lifestyle and mindset.
This is particularly valuable and insightful if you start looking at generational differences.
Each age/generation (baby boomers, Centennials, Generation Z, Generation X, Millenials, etc) has certain major characteristics that define them.
What activities do they participate in?
How they view the world?
How to the view a career?
What is important to them?
What are their underlying beliefs and patterns?
With these details, you can figure out what they search for online and create targeted content around it.
v. Gender
Sites that target a specific gender can be more successful than other sites, since their audience will likely have more uniform sets of interests.
By understanding the gender-specific interests, you can target the right types of keywords and produce highly relevant content every time.
vi. Personality
Sometimes, the topics you choose might be only interesting to people of certain personality traits.
For instance, people searching about social anxiety might be have a tendency to be introverts.
In addition, certain occupations are dominated by specific personality types.
Once you understand this, you can figure out a broad range of keywords that those types of groups would search for online.
vii. Education Level
How you write about an issue can influence the kind of people who read it.
For instance, a basic discussion on politics will pull in the general public.
However, an in-depth analysis of scientific studies regarding political activity will likely bore the everyday person.
But it will capture the interest of graduate students researching the subject.
If you’re targeting people highly educated in a specific niche, you must incorporate a range of keywords that include in depth technical language and ideas.
You’ll have to know your topic inside and out as well.
viii. Political Affiliation
Many sites that discuss political topics focus on content suited to people with specific political affiliations.
Just look at the news.
This means understanding the political views people value, that way you can uncover the terms they likely search for on Google.
ix. Religious Affiliation
This can be particularly valuable and cause traffic spikes during religious holidays or major events affecting your audiences’ religion.
If you have an eCommerce site, you can set up special offers during religious celebrations when people typically shop more.
You would then target types of keywords that experience a spike during that celebration.
If you have deep religious convictions (as I do), I recommend writing about it and incorporating it into your site.
It can be a point of connection between you and your audience.
Will it turn some people off?
Yes.
But that’s okay.
x. Nationality/ Location/ Geo-Targeting
You’ll often have an easier time crafting relevant content if your site has a uniform focus on one nationality or location.
Keep in mind, geo-targeted keywords aren’t just keywords that contain the location name.
Some general keywords actually have more searches within certain locations than others, typically based on what the people in those locations are mostly interested in.
If you know what the people in your target location are most interested in (compared to other locations), you can easily find the right keywords they search for.
For example, I live very close to Legoland Florida and Disney (right smack in between them both).
So those would be huge local keywords for people trying to target the visitors to our area.
Here’s how you can find keywords for specific locations you’re targeting.
First, find one keyword that has the highest search traffic in your target location.
That will take a bit of effort if it’s not as obvious as my Disney and Legoland example.
Start by checking through the location-specific search traffic of multiple keywords in Google Keyword Planner.
It’s best to start with a low-search-volume keyword that contains the target location.
Let’s use this site as an example.
My site is about network marketing.
I could start with the the term “top network marketing companies in USA.”
Input your keyword in Google Keyword Planner and change the location setting to your target location.
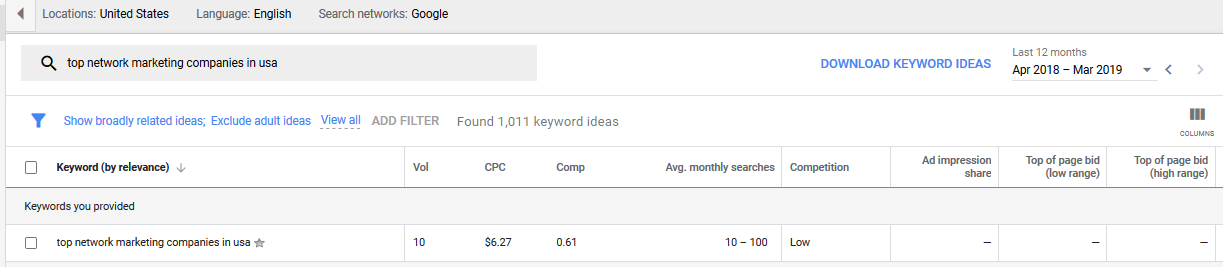

Secondly, with the settings still focusing on your target location, check through the keyword ideas.
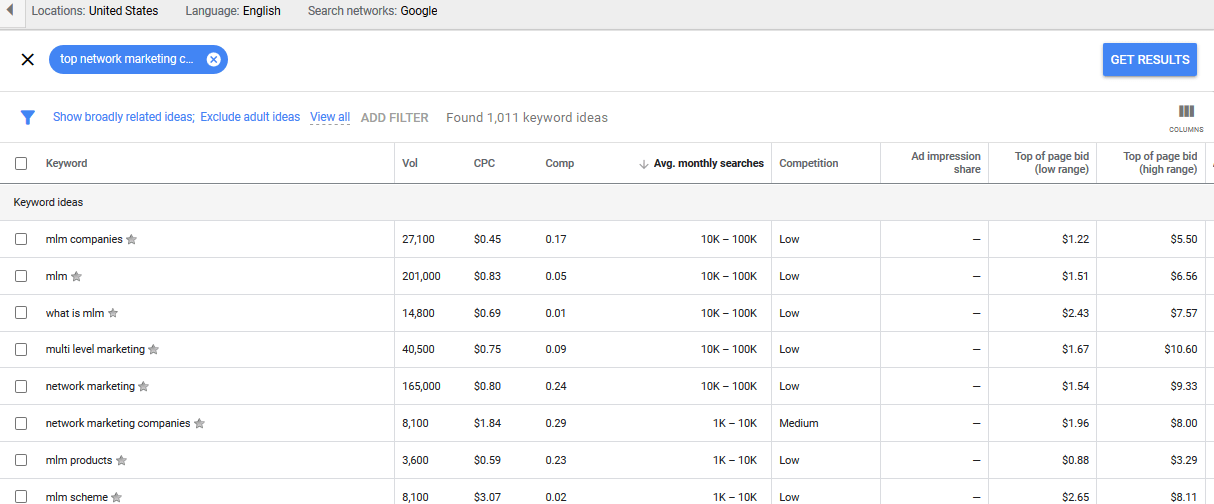

Pick each keyword idea, one-by-one and check them individually through Google Keyword Planner to find the search volume they have within your targeted location.
Then pick the ones that have the greatest search volumes within your target location compared to all other locations.
Considering the amount of work required to do this, you can simply identify a few high-volume keywords that you’ll base your overall site on.
xi. Disabilities/ Challenges
Certain challenges can unite people of varied genders, nationalities, political affiliations, and so on.
In such instances, your content shouldn’t target keywords restricted to specific groups.
Instead, focus on the unifying challenges.
Do that by identifying key terms people affected by the challenges universally search for.
If you suffer from a particular challenge, health problem, or disability you can really connect with (and help) others by having the courage to talk about it and/or write about the struggles you’ve had.
There is connection in authenticity.
xii. Race/ Culture
Certain issues may concern a specific race of people or cultural group, usually regarding awareness campaigns.
Understanding the unifying characteristics of that group will help you figure out what they search for on Google.
You may also find that certain general topics attract a specific community.
If you happen to notice this in your keyword research, then focus in on that and see if there are keyword strands you can benefit from that aren’t highly competitive.
xiii. Marital Status
Some products are predominantly purchased by married couples such as marriage retreats or couples therapy.
Therefore, you can target that group by figuring out the main concerns they have and crafting your content along those lines.
Consider your audience.
Are you writing for couples who:
- Fight too much but want to stop?
- Are planning a vacation together?
- Are in business together?
- Are struggling with raising a family?…
You get the idea.
Start with the audience, then move on to the keywords that would benefit them and help them find a solution for a problem.
xiv. Mortgage / Living Status (Homeowner or Renter)
If you’re doing affiliate or online marketing, you need to match the products you recommend to your audience.
So if you’re recommending a home renovation service, you need to target homeowners.
Renters will have little interest in home renovation because it wouldn’t make sense to dump money into something that isn’t theirs.
That means your content should be crafted around the key issues homeowners search for online.
On the other hand, if you’re targeting renters, you would want to craft a message about something that renters would potentially struggle with.
xv. Users’ Emotional State
This can be a powerful thing to consider when marketing products online.
Try to figure out the emotional state of customers when they purchase your products.
For instance, someone going for repair services is probably upset and distressed.
Hence, they’re probably searching for fast results to quickly end their suffering.
They are also probably looking for reviews.
Who should they go to?
Who’s the cheapest?
Who’s the best?
Who’s the most honest? Etc.
In addition, as you progress in your marketing journey, you’ll want to learn how to move people to an emotional state that converts.
Rarely will somebody just show up ready to buy (unless you’re a company like Ebay or Amazon).
So keep that in mind as you’re writing.
People make decisions based on emotion and back it up with logic… not the other way around.
5. Category/ Niche Based Keywords
When you see the search volume of a keyword, it might include not just searches within your niche, but also within other niches.
So you need to find keywords whose searches are predominantly within your niche.
If you don’t do this, you might never realize the search volumes you expected.
Fortunately, you can do it using Google Trends.
Here’s how.
i. Limited Category/ Niche Specific
If you want to be sure that all or most of the traffic for a specific keyword comes from within your specific niche, check the search trends in the different categories in Google Trends.
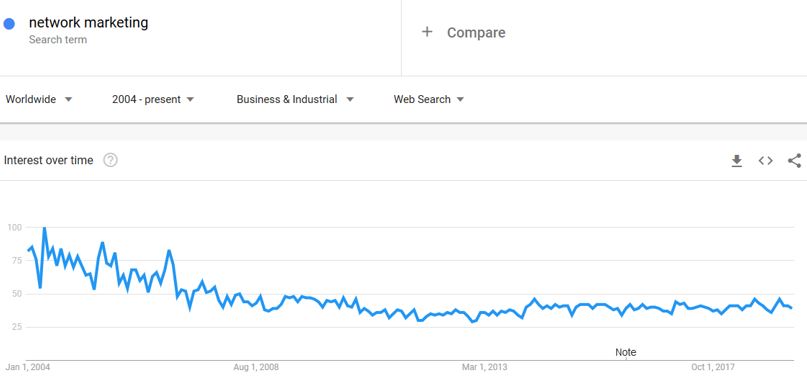
As you can see here, most of the searches for the keyword “how to succeed in network marketing” are concentrated in the category, “business and industrial.”
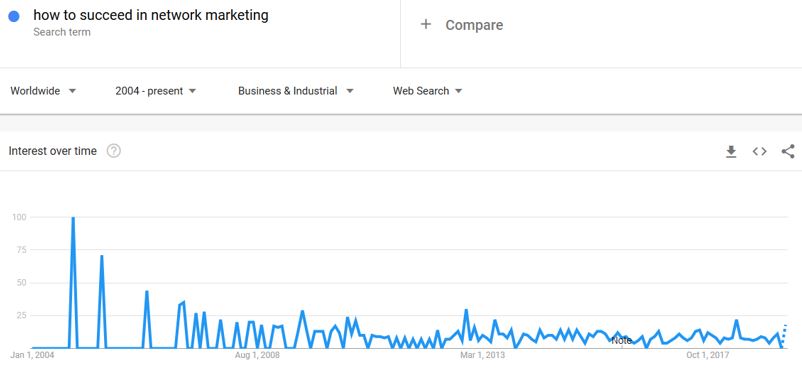

You can hardly find any search trends for that keyword in any of the other categories, such as arts and entertainment:
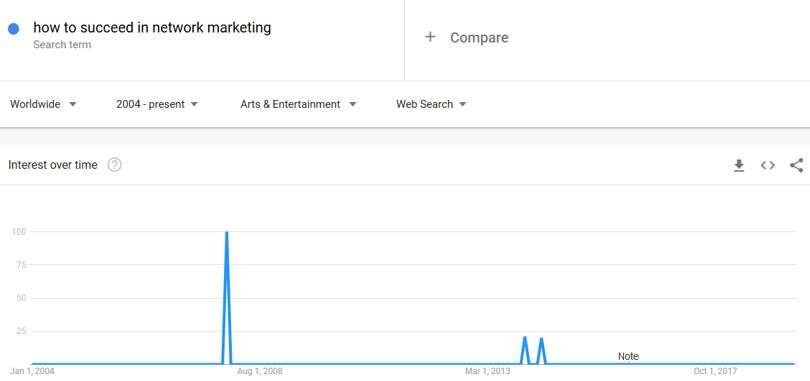

That shows that the keyword is highly niche specific, and most of the search traffic lies within one niche.
ii. Uniform Cross-Category
Other keywords are not niche specific.
They apply across multiple niches.
That means the search traffic you see for that keyword would be divided across many different niches and multiple audiences.
The result is your site would probably not get the full effect of that traffic.
Again, let’s use the term “network marketing.”
As you can see, it has a search trend in the category “business and industrial.”

But the same keyword also shows a search trend in the other categories, including arts and entertainment.
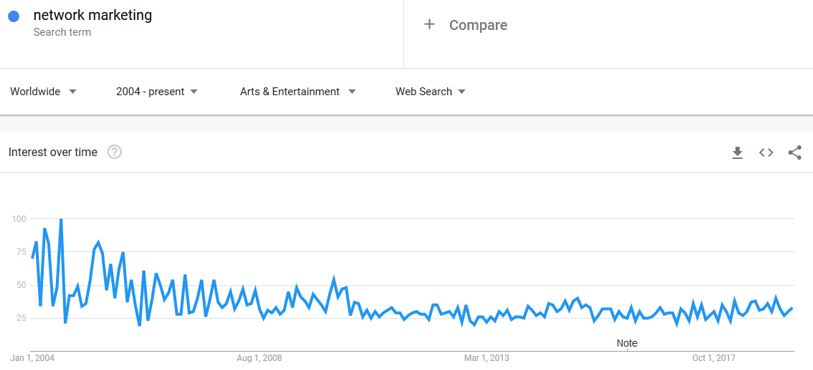

Such keywords can still be useful if you’re targeting audiences in multiple sectors, or you want to expand your audience.
iii. Cross-Category Diversification
Here’s where things get even trickier.
Apart from having the search traffic coming from multiple niches, the actual keyword itself might have more than one meaning in the different categories.
That means you won’t get the maximum traffic, plus the keyword won’t be relevant to some of the audiences searching for that keyword.
A simple example is the search term “apple” that I mentioned earlier.
In the technology niche it refers to a company, but in the food niche it refers to a fruit.
In some instances, you can actually incorporate the diverse meaning of the keyword in one article.
iv. Related Niche Queries
When you identify a keyword that’s highly specific to your niche, you should also leverage that finding by checking out the queries related to that keyword (in Google Trends).
This makes your work easier in finding keywords that are specific to your niche.
For instance, the phrase “network marketing jobs” is largely concentrated within the business and industrial niche.
It has the following related queries, which are likely specific to the same niche:
- network marketing companies
- what is network marketing
- food network jobs
- network marketing in India
- food network
- network rail jobs
- Indeed
- big shoes network
- weather network
- empower network
6. Site Structure
Once you have a niche, you shouldn’t just target any random types of keywords for your SEO optimization.
You should be methodical in your keyword choices, so that anyone visiting your site will know what to expect from you.
Be assured, Google will know exactly how to categorize your overall site.
This structure should be evident in your overall website and in each article.
i. Hub and Spoke Keywords
The hub and spoke keywords apply in the overall website structure.
This simply means building your site based on a major keyword or phrase (the hub) and creating content around it that caters to multiple aspects of that word or phrase (the spokes).
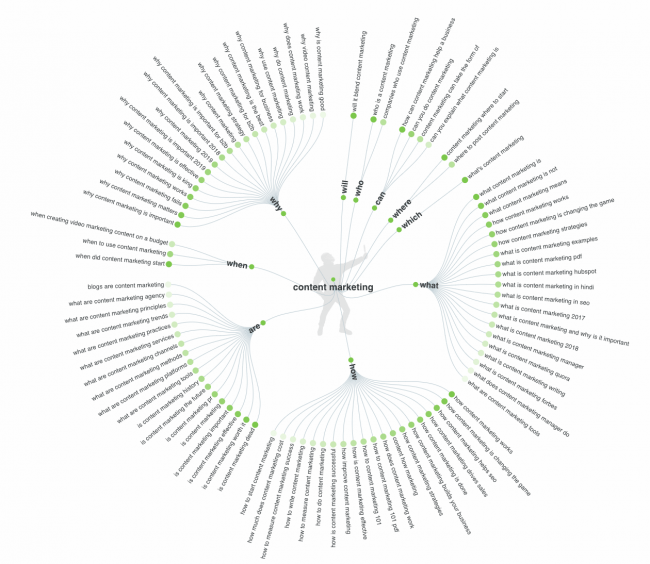

With this strategy, even if the major keyword is hard to rank for, you’ll eventually do it based on the topical relevance produced by continuously creating content around the minor aspects.
ii. Content Words
Understanding the hub and spoke strategy is essential for proper SEO optimization.
That way, you won’t optimize your content for keywords that won’t benefit your overall website.
Follow these SEO Rules for Each Article:
- Have a primary keyword which is a spoke keyword in the overall website structure (e.g. ‘what is content marketing’).
- Include secondary keywords which bear similar meaning and words as the primary keyword (e.g. ‘content marketing vs. digital marketing’).
- Feature tertiary keywords which have similar meaning as the primary keyword but different words (e.g. ‘writing blog posts’).
- Place random keywords which cover random issues related to the primary keyword (e.g. ‘top content marketer’).
7. SEO Optimization Keywords
Once you cover the foundational content of your website, you can then further tweak your content for higher ranking and improve your site value.
Here are some types of keywords to consider.
i. Negative Keywords
Not all keywords are good ones.
Your content should be highly specific and linked to your main keyword; therefore, you need to weed out keywords that are irrelevant or don’t match user intent.
Google evaluates your content to best align it to search results so you should eliminate content that makes Google’s task harder.
ii. Shorter Bounce Rate
If you want people to spend more time on your site, you need to put up the type of content that keeps them there longer.
You can figure out what content falls into this category by doing a comparison with low-bounce-rate sites in your niche.
If you find certain keywords that you’re missing, they’re probably what you need to add to your site.
You can use various website analysis tools to analyze bounce rates, like Alexa.
You can also take a look in your google analytics account (which you should definitely have set up)
iii. Promoting your Brand
If your competitors are way ahead of you, they may already get searches based on their brand names.
If so, learn how you can take advantage of that.
You can have posts that compare your services/products with that of your competitors.
You can even do a review of the competitor to show what you can do better.
When people search for your competitors’ brand names, they’ll also find your content.
You have to be careful with this strategy because people are people.
I would first suggest reaching out to you competitors and see if you can work with them or do something to earn a link from them.
That way Google will see that their site (high authority) finds value in your site and you can get some link juice.
If you do try to siphon off some of their traffic, make sure you aren’t bashing them.
You never want to burn bridges, you might be able to work with them in the future.
iv. Ranked Keywords Missing in Content
Once your content starts ranking on Google, you’re sure to benefit if you include keywords or phrases that you’re already ranking for, but don’t specifically have in your content.
That simple strategy can boost your rankings and traffic quite a bit.
The best way to do this is to look at your Google search console to see what those phrases or words are.
v. Unique Keywords
Although it’s hard to find, some keywords literally have zero or extremely limited content about them.
These are typically low-volume keywords, but you shouldn’t dismiss them.
Once you write content around these gems, you’ll have a pretty good chance of ranking high even without backlinks or without having a high authority site.
And soon, your traffic stats will increase as your content picks up ranking for other keywords.
To find such unique keywords, you’ll need to test multiple searches; especially long-phrase terms or terms that have uncommon combinations of different words.
You can also search for keyword ideas in Google Keyword Planner (check through long keywords, keywords with low volume, keywords with low advertiser competition, or keywords with low CPC).
vi. Rare Keywords
These are keywords that aren’t particularly unique, but have minimal content around them.
So, the keywords that don’t make the cut from your search for unique keywords would be your rare keywords.
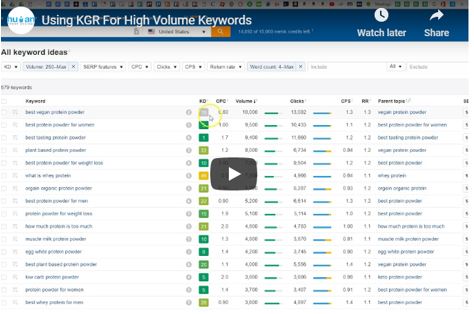
vii. Keyword Golden Ration (KGR) Keywords
Similar to unique and rare keywords, KGR keywords are designed to gain Google ranking without Backlinks.
This requires an extensive tutorial to know how to apply it so check out this video from the creator to learn how:


As you may notice, the KGR strategy applies to keywords with a maximum monthly search volume of 250.
For keywords with higher volumes than 250, you’ll apply the Rule of 63, as illustrated in this video:
viii. Futuristic Keywords (a.k.a. – Keywords of the Future)
This is another strategy to put you ahead of the competition and it will take some thinking on your part.
It simply means featuring keywords that don’t exist yet, but will in future.
They may include keywords that mention a particular year.
When Google indexes your content, it can rank you high for that keyword.
You’ll likely get top ranking position for a long time before people start searching for it and other sites start including it.
A good example of this is our post about the best network marketing company to join in 2019.
Depending on when you’re reading this, the year may be different.
It was written and published in November or 2018 because I know the beginning of the year is a time people want to make changes.
I published it in November to give it some time to rank before Jan. 1st.
Knowing what I know now, 2 months to rank is not enough time, but that was my plan.
In addition, I did NOT include the year in the URL.
The URL extension is… /best-mlm-to-join.
This will allow me to update it every single year a few months out to be ready for the new year.
So I’ll change it to the best mlm to join in 2020 at the end of this year and so on and so forth.
It worked beautifully.
I get some traffic (not #1 yet) and I anticipate that traffic will increase every year and my rankings will climb.
This is because I won’t be starting from scratch each year.
By changing the year in the title and article, I am able to capitalize on the ranking power I already have.
This year I already rank for some terms so I will just be building on the foundation I already built.
ix. Historical Keywords
As many websites update their content, they probably get rid of keywords they featured in the past.
However, there might still be people searching for those historical keywords.
Take advantage of that.
Try not to lose or ignore keywords you already got credit from Google for (even if it was accidental).
Capitalize on it the best you can.
x. Keywords of Most Commented Articles
When people comment on your article, they not only stay longer on your site, but also add valuable keywords to help your page rank even higher.
You’re literally getting free content.
Therefore, you need to find topics that people often comment on in your niche.
When you find articles that get extensive comments and you can figure out the keywords they rank for, you’ll be able to pull in the same type of people that frequently comment on articles.
This isn’t a strategy I’ve used to much yet, but if I start getting some traction on a particular post I’ll certainly be ready.
xi. Keywords of Most-Shared Articles
Certain topics tend to get shared a lot.
This also has to do with the type of people who search for the articles and read them.
You can analyze the keywords of those most-shared articles, see what they rank for, and build your content around them.
xii. Keywords of Most-Backlinked Sites/ Pages
When bloggers are researching online for resources to link to, they are likely to pick the top-ranked pages they find.
Hence, if you find an article with numerous backlinks, it’s probably because it ranked top for specific keywords.
Targeting those keywords can also put your content on top for other bloggers to find and link to.
There are a number of ways to build backlinks but any organic backlinks you can get are powerful.
I suggest having great infographic.
Some of my greatest backlinks have come from infographics.
xiii. Keywords of Articles Getting High Traffic
It may not be possible to determine how much traffic specific competitor pages get.
However, some websites still indicate the amount of traffic they get on each page.
Once you find pages that get high organic traffic, you too can target the same keywords to tap into that traffic.
You could also use SEMRush to do some competitor spying.
xiv. Keywords of Small Sites That Outrank Big Competitors
Often, you don’t need to re-invent the wheel or be the first to start something new.
“Mr. Wonderful” from shark tank likes to say “Pioneers get slaughtered, settlers prosper”.
You can get ideas from others who have done something extraordinary.
If you find a small site outranking much bigger and established competitors, or a new site picking up super fast, the site is probably doing something out of the ordinary and effective.
It may be targeting keywords that the competitors have no idea about.
If so, you can borrow those same ideas.
In fact, the site you borrow from doesn’t even have to be within your own niche.
You can borrow ideas from sites in other niches and adapt the concepts to your specific situation.
xv. Google Image/ Video/ Voice/ News/ Maps/ Books/ File Type Search Keywords
Your article can have more than just written content.
It can also have images, video, maps, news stories, books and even downloadable files (PDFs, spreadsheets, Word documents…)
But don’t stop there.
People have to know that your content has such items; otherwise, they won’t find them.
That means including keywords that specifically apply to those items.
For instance, a keyword phrase like “your first year in network marketing pdf” would be a good fit for me.
Besides, some keywords may not have specific terms that indicate someone is searching for similar content types.
Again, you can find keywords like this through Google Trends.
When you analyze general keywords in Google Trends, change the settings to show search trends under Google images or news.
Then, scroll down to the related queries, which will show keyword ideas that people searched for in Google images or news.
xvi. Multilingual Keywords
Google Keyword Planner has the option to find keywords in multiple languages.
This can be useful if you want to create a second site in your niche, but target people who speak a different language.
You can literally translate your website content and get a different set of audience.
If you’re wondering whether that would lead to a Google penalty, it doesn’t, as long as it’s a human translation:
xvii. Other Search Engine/ Forum/ Social Media Site Keywords
Although you may not directly use keywords from other search engines, forums, and social media sites, they can give you new keyword ideas you haven’t explored or thought of.
You can use those ideas to find keywords that apply to Google.
After all, often when a topic trends in social media, people will go on Google to search and find out more on the topic.
xviii. Low/ High Difficulty Keywords
Low difficulty keywords are simply keywords that are easy to rank for compared to high-difficulty keywords.
With low difficulty keywords, the top competing pages ranking for the keyword have low page authority, low domain authority, few backlinks on the page, few backlinks on the site, and minimal social media shares.
High difficulty keywords have the opposite characteristics, and they typically have higher traffic potential as well.
When starting out, you’ll likely target low-difficulty keywords.
As your site’s domain authority grows, you can then target higher difficulty keywords, since you’ll have a better chance of ranking for them.
This is also a consideration to make when updating your content. If the page gains higher authority after publishing, you can update your article to target higher difficulty keywords.
xix. Related Query Keywords (from Google Trends and Google SERPs)
The related queries you find in Google Trends for your target keyword can play a significant role in getting your content to rank high.
The related queries typically show keywords that people most often search for alongside your target keyword.
It’s what everyone does when searching on Google.
Let’s suppose you search for a term like “make money.”
When you see that the results aren’t exactly what you want, you do a further search for the term “make money fast.”
If many people do that, Google sees it and incorporates the results for the term “make money fast” into the results for the term “make money.”
The powerful effect of these types of keywords in SEO can even outdo pages with more backlinks but lacking those related queries.
xx. Competitor Keywords
To remain competitive, you can incorporate keywords that your competitors have.
However, do this carefully.
You should consider the ultimate goal of your site before copying what competitors are doing.
Don’t just copy anything and everything competitors do.
Identify the keywords that will help you achieve your own goals and use those.
xxi. Long and Short Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords are keywords with low search volumes and short tail keywords are keywords with high search volumes.
It’s often easier to rank for long-tail keywords since such keywords tend to have long phrases that few sites feature in their content.
However, there are three other opportunities you can take advantage of:
- Identify short-tail, high-volume keywords that are made up of long phrases. Since they are uniquely long phrases, you might find that few sites have such keywords.
- Even when you target long-tail keywords, try to find those that have a high-traffic root keyword. For instance, the long tail keyword, “how to make money in London” has only 390 monthly searches. But, its root keyword “how to make money” has 201,000 monthly searches. This way, as you rank for the long tail keyword, you can also tap into the higher traffic of the root keyword.
- You can also target short long-tail keywords. You might find that many sites don’t bother with the keyword since it has low search volumes.
xxii. High Click-Through-Rate Keywords
The keyword, “time” has about 7 million monthly searches, but it probably has an extremely low click-through-rate.
That’s simply because Google gives users the exact time, based on location…. which is what users are probably looking for.
They don’t need to click on any of the search results.
So don’t waste time optimizing for these types of keywords.
Instead, look for keywords that are likely to have a high click-through-rate.
This is becoming increasingly difficult because google is starting to put drop down menus with answers in their search results.
xxiii. SERP Feature Keywords
Google shows different kinds of SERP features for multiple keywords.
The SERP features include:
- featured snippets
- image packs
- in-depth articles
- knowledge cards
- knowledge panels
- local packs
- local teaser packs
- news boxes
- related questions
- reviews
- shopping results
- site links
- tweets
- videos
You can target the keywords that show such SERP features and optimize your content to appear in them.
xxiv. Device-Based Keywords
Some keywords are more likely to be searched for on specific devices (yes, really). These include mobile phones, laptops, tablets, and desktops.
It may also vary based on the operating system or browser on the device.
Sometimes it’s just a coincidence but it’s good to know. My site get’s the most visits from mobile phones and visitors to my site are mostly Apple users.
So it’s more important for me to make sure my pages display right on an iphone than an android.
This may be a result of my habits more than my users. I have an iphone and I check my site through it.
If I see a problem I fix it.
That may have made the experience better for iphone users and could very well be the cause of most my users being ihpone users.
It’s something to take into account though.
You can get such insights from your website’s Google Analytics.
Then optimize your content for the best experience on the particular devices.
xxv. Dynamic Keywords
Unlike static keywords, dynamic keywords change over time. The new keyword that replaces an old keyword takes over the old keyword’s traffic.
This is especially so for keywords with years.
It also applies with informal language that typically has constantly changing words.
You need to just be aware of this so if your traffic starts going down for a particular page, you can take a look and see if some of the terminology has changed over time.
If so, just update the content to reflect the change and google should fix the indexing issue.
8. Revenue Optimization Keywords
If your goal is to maximize revenue, you can use specific keywords to do that.
i. High Value/ Low Value Keywords
Many advertisers will target keywords that produce high conversion rates or greater revenue.
So, high value keywords can help you achieve the same thing through organic rankings.
Identify high value keyword by checking:
- keywords with high advertiser competition in Google Keyword Planner
- keywords with higher CPC
- keywords with higher top of page high and low bid ranges
ii. Google Shopping Search Keywords (Buyer Intent Keywords)
These are likely keywords people use when they are ready to buy and you can (and should) target them too.
When analyzing keywords in Google Trends, change the settings to show trends of searches people made of the keyword in Google Shopping search.
Then scroll down to the related queries where you’ll find keywords people search for in Google Shopping.
iii. Amazon Keywords & Other E-commerce Site Top Seller Keywords
E-commerce sites like Amazon can give you great ideas of buyer-intent keywords related to your niche.
Simply check on the keywords people use to find top-seller products on the e-commerce sites.
Then use them as ideas to find similar keywords in Google Search.
9. Traffic Flow Keywords
If you want to stabilize your site and get consistent traffic, you must assess the traffic flow of your keywords.
Augmenting the different types of keywords here will do the trick.
i. Trending, Short-Term, & Fresh Keywords
Google Trends gives insights on the highest searched terms in the day or within the past 24 hours.
You can even check for trends within different locations.
Regularly check through the trends so you can take advantage of topics that specifically apply to your niche.
However, many trending topics may not be directly related to your niche.
But you can craft content that makes them relevant, and benefit from the traffic spike.
ii. Seasonal Keywords
Some keywords have seasonal spikes interchanging with low traffic seasons.
To get a constant flow of traffic from such keywords, you can target different keywords with varying seasonal spikes.
This way, you’ll get traffic from one set of keywords when the other is experiencing a lull in online searches.
Using Google Correlate, you can find keywords that have matching spikes and dips:
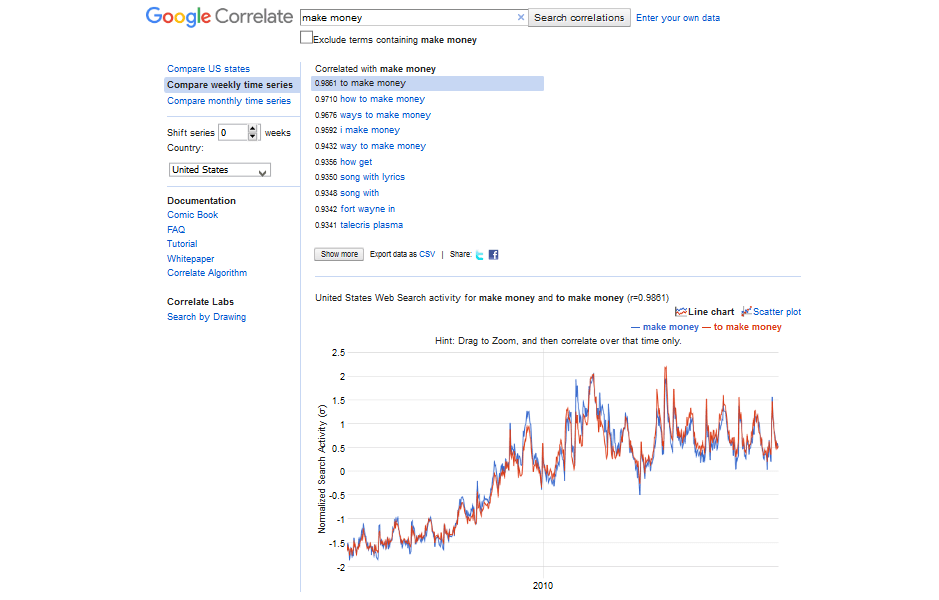

When you download the keyword data, reverse the search trend (turning the spikes to dips and vice versa), and upload to Google Correlate, you’ll get keywords that have an opposite trend of dips and spikes.
iii. Evergreen Keywords
Evergreen keywords are the most consistent types of keywords in SEO.
Search volumes for these keywords don’t experience erratic dips and spikes. And they remain consistent for many months and years.
The search phrase “where to buy a Christmas tree” would obviously be seasonal where something like “how to make money on youtube” would be move evergreen.
iv. Dying or Growing Keywords
When looking at the traffic potential of keywords, always consider the long-term traffic trend.
Some keywords might be experiencing a long-term dip in traffic, which won’t be evident from a one-year trend.
Check in Google Trends to see the longer 5, 10, or 15-year trend data.
Then look for keywords that have a growing long-term trend.
10. Inverted SEO Optimization
What if you take SEO and turn it upside down?
Instead of targeting keywords that already exist and already have traffic… why not create those types of keywords and then target the traffic?
That way, you’ll be the first to rank for that keyword and most likely people will always click to your site since you are the creator.
Actually, this isn’t a new thing, since it’s what companies do when they create a brand.
Nobody searched for wikipedia until wikipedia meant something.
Once you have a unique brand name, people will search for that name and will intentionally click through to your site.
That’s why your site should have unique and memorable name.
You can do that by leveraging these types of keywords in SEO.
I took this approach when creating this site.
I could have branded my name but I’m setting up a legacy for my kids, their kids, and their kids.
Someday, when I exit this physical body and go be with the Lord, I want them to inherit a brand, not a website of my name.
Imagine what this site will be if it is carried on from generation to generation.
That being said, I also understand basic SEO optimization around types of keywords.
In SEO, the first few words carry the most weight.
It’s not by accident that the first real word in my site name is wealth (wealth-anize).
Over time, this site will be given more weight for things having to do with wealth buiding, especially since much of my content is on that topic and it’s also in the site name.
But if you want to see the power of the inverted SEO optimization technique, simply go to google and do a search for wealthanize.
You’ll see that our site and social channels dominate the page and the results.
It’s not because we’re soooo good.
It’s because it’s not a real word…. we made it up!
It’s a simple hack that works well and will probably work well for a long, long time.
i. Modified Keywords
This is the easiest inverted SEO keyword to rank for.
You’ll leverage on an existing keyword by adding a new word to it, making it unique.
This way, you’ll tap into the existing traffic for that keyword.
When people find that modified keyword the first time, they’ll likely search for the exact phrase the next time.
The real-estate site biggerpockets does this effectively.
It’s two words put together that is also a phrase referring to making more income and filling your pockets (so they are bigger).
ii. Niche-Transfer Keywords
This is what Apple, the company, achieved by taking the name Apple, the fruit.
Here, you take a keyword from one niche that means one thing in that niche, and apply it in another niche to mean something different.
You can then leverage the existing traffic for the original keyword using different strategies, such as by making a comparison post.
For example, you may write a post like, “10 characteristics that Apple (the company) shares with apples (the fruit).”
iii. Throwback Keywords
These keywords may not have much traffic potential, but you can leverage on their nostalgic value.
Some topics go out of fashion and people stop blogging about them.
That means if you write about these topics and re-ignite interest about them, you’ll likely gain top ranking for the related keywords.
iv. New Keywords
This is the toughest keyword strategy of all the SEO optimization techniques, but one of the most beneficial.
It involves creating a completely new word based on a new technique, product, brand or anything else.
You’ll have to create interest for that keyword, but you’ll likely be the top beneficiary of the search traffic if it catches on.
We’ve attempted to do that with our article I mentioned earlier on “collateral traffic”.
Most terms on SEO optimization and website traffic are highly competitive.
But by putting collateral and traffic together, I’ve created a new name for a strategy.
Anytime somebody searches for it, I’ll likely be high up on the Google ranking totem pole.
This is because as the term naturally gains interest and organic traffic, it will also be gaining organic backlinks from other sites.
By the time it has a good google search volume and somebody wants to write about it, I’ll have a head start and tons of backlinks.
That will keep me #1 for a long time for that keword phrase.
Conclusion
With these types of keywords, you can craft the right content and achieve the best results for your site.
You’ll also know the best way to adjust your content based on the types of keywords for SEO optimization.
If you currently have a site or blog that you’re trying to monetize better, we help bloggers monetize their site and are always looking for people to partner with.
Reach out to us and let’s discuss how we can help you.
Keep moving forward and remember:
If nothing changes…. nothing changes.
Lastly, if you’d like a personal relationship with Jesus Christ, go here: JOHN 3:16


Jason & Daniele